In today’s world where corporate data volumes are increasing exponentially, extracting meaningful information from this data has become one of the fundamental ways to gain competitive advantage. Descriptive Analytics is the most basic and widespread analytical approach that enables organizations to make sense of their data heaps. This type of analytics answers the question “What happened?” providing valuable insights about past events and forms the first stage of data-based decision-making processes.
Core Components of Descriptive Analytics
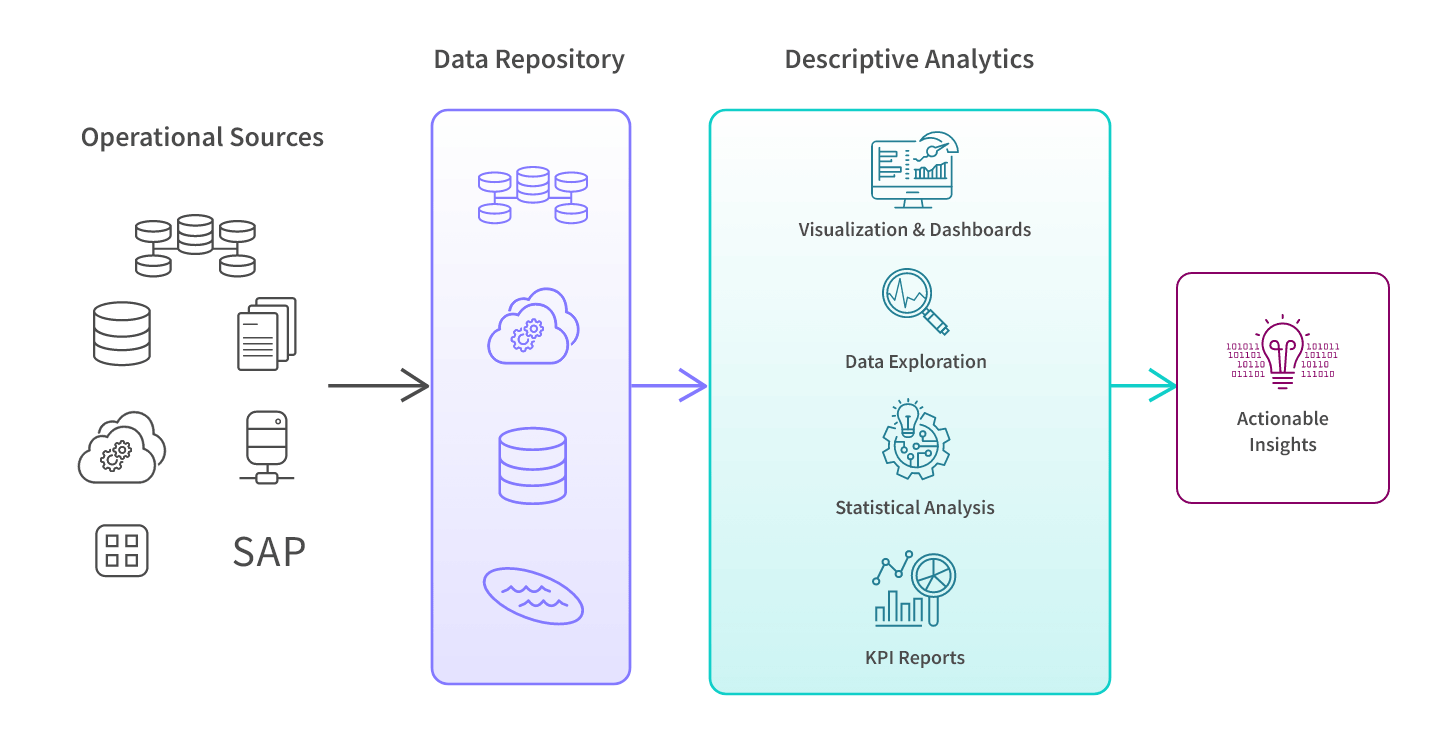
Descriptive Analytics encompasses a series of methods and techniques that transform raw data into meaningful information. The core components of this type of analytics form a process chain extending from data collection to the presentation of meaningful insights.
Data Collection
The first stage of descriptive analytics is collecting data from different sources. This data can come from numerous sources such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, websites, social media, and various sensors. Quality control mechanisms are applied during the data collection process to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the data.
Data Processing
Collected raw data is usually not in a suitable format for analysis. In the data processing stage, data is cleaned, transformed, and prepared for analysis. This process includes handling missing values, detecting outliers, data normalization, and standardization.
Data Visualization
Processed data is converted into visual formats such as graphs, tables, maps, and dashboards. Data visualization enables easy understanding of patterns and trends in complex data sets. Effective visualizations facilitate the sharing and understanding of data insights across the organization.
Data Summarization
The final component of descriptive analytics is summarizing the data. At this stage, large data sets are summarized and presented in the form of key performance indicators (KPIs), trend analyses, and comparative reports. Data summarization provides decision-makers with quick and actionable insights.
Descriptive Analytics Techniques
Descriptive analytics uses various techniques for understanding and interpreting data. These techniques are designed to reveal patterns in data sets and provide meaningful insights.
Summary Statistics
Summary statistics are numerical measurements that summarize the basic characteristics of data sets. Statistics such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, minimum, and maximum values provide important information about data distributions. These measurements help us understand the basic properties of large data sets.
According to Gartner’s 2023 report, 75% of companies using descriptive analytics to leverage summary statistics reported significant improvements in their decision-making processes.
Data Clustering
Data clustering is a technique that groups data points with similar characteristics. This technique is widely used in applications such as customer segmentation, product categorization, and market segmentation. Data clustering enables better understanding of target audiences and development of more personalized strategies.
Reporting
Reporting is among the most basic and common techniques of descriptive analytics. Regularly generated reports provide valuable insights on topics such as sales performance, financial results, operational metrics, and customer behaviors. Modern reporting solutions create interactive and dynamic reports, enabling users to interact more effectively with data.
Dashboards
Dashboards are visual interfaces that allow monitoring the organization’s performance in real-time. An effective dashboard supports quick and informed decision-making by enabling at-a-glance viewing of key performance indicators (KPIs). Dashboards are usually customizable, so they can be adapted to the specific needs of different business units and users.
Differences Between Descriptive Analytics and Other Types of Analytics
Descriptive analytics is just one part of the analytics spectrum. Compared to other types of analytics, descriptive analytics has its own unique features and applications.
Descriptive vs Diagnostic Analytics
While descriptive analytics answers the question “what happened?”, diagnostic analytics focuses on the question “why did it happen?”. Diagnostic analytics requires deeper analyses to understand the root causes of events. Descriptive analytics summarizes past performance, while diagnostic analytics examines the factors behind this performance.
Descriptive vs Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics tries to predict future events using past data. It aims to answer the question “what could happen?”. While descriptive analytics focuses on understanding historical data, predictive analytics uses this data to create forecasts about the future.
Descriptive vs Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics aims to suggest the best action based on predictions. It answers the question “what should we do?”. This is the most advanced form of the analytics spectrum. While descriptive analytics helps understand the current situation, prescriptive analytics identifies the steps that need to be taken to achieve optimal results.
Benefits of Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics provides organizations with many important advantages. These benefits improve business performance by enhancing data-driven decision-making processes.
Business Intelligence Enhancement
Descriptive analytics enhances business intelligence by providing valuable insights about the organization’s business processes and performance. These insights enable decision-makers to better understand the current situation and make more informed decisions.
Real-Time Insights
Modern descriptive analytics solutions offer real-time data analysis capabilities. This allows organizations to quickly respond to market changes, customer behaviors, and operational issues. Real-time insights can offer a significant competitive advantage, especially in rapidly changing sectors.
According to McKinsey’s 2024 report, companies using real-time descriptive analytics have achieved increases of up to 33% in customer satisfaction.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Descriptive analytics encourages data-driven decision making instead of intuitive decision making. Data-driven decisions typically produce more accurate and effective results. Descriptive analytics provides decision-makers with the information they need to accurately assess the current situation.
Performance Measurement
Descriptive analytics provides a powerful tool for performance measurement at different levels of the organization. Key performance indicators such as sales targets, production efficiency, customer satisfaction, and financial results are regularly monitored to identify areas for improvement.
Descriptive Analytics Use Cases by Industry
Descriptive analytics has various applications in different sectors. Each sector creates value by adapting descriptive analytics to its specific needs and challenges.
Descriptive Analytics in the Financial Sector
Financial institutions extensively use descriptive analytics in areas such as risk management, customer behavior analysis, and financial reporting. Descriptive analytics enables monitoring financial trends, detecting abnormal transactions, and customer segmentation.
A global banking organization improved fraud detection by 40% and reduced operational costs by 15% by implementing descriptive analytics solutions.
Descriptive Analytics in the Retail Sector
Retail companies use descriptive analytics in areas such as inventory management, sales performance analysis, and customer behavior monitoring. Insights based on sales data and customer demographic information enable more effective marketing strategies and product placement decisions.
A retail giant optimized in-store product placement using descriptive analytics solutions, resulting in a 22% increase in sales.
Descriptive Analytics in E-Commerce
E-commerce platforms use descriptive analytics in areas such as website traffic analysis, conversion rate optimization, and customer journey mapping. These analyses provide valuable insights for improving user experience and increasing sales.
A leading e-commerce platform reduced cart abandonment rate by 25% and increased average order value by 18% using descriptive analytics tools.
Descriptive Analytics in the Manufacturing Sector
Manufacturing companies use descriptive analytics in areas such as production line performance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. Production data and quality metrics are analyzed to identify opportunities to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
An automotive manufacturer used descriptive analytics solutions to identify bottlenecks in the production line, increasing production efficiency by 20% and reducing product delivery times by 30%.
Descriptive Analytics in Telecommunications
Telecommunications companies use descriptive analytics in areas such as network performance analysis, customer churn prediction, and service quality monitoring. Network data and customer usage patterns are analyzed to optimize infrastructure investments and customer satisfaction strategies.
A telecommunications leader’s application of descriptive analytics reduced customer churn rate by 35% and significantly increased customer lifetime value (LTV).
Tools and Technologies for Descriptive Analytics
The success of descriptive analytics applications depends on using the right tools and technologies. Qlik is a comprehensive business intelligence and data analytics platform that is a leader in the field of descriptive analytics.
Qlik Business Intelligence Platform
Qlik is a powerful business intelligence platform that enhances organizations’ data discovery and visualization capabilities. With products like Qlik Sense and QlikView, it allows users to analyze their data in an interactive and intuitive way. Qlik’s patented associative data model enables users to explore relationships between data and uncover hidden insights.
Qlik’s Data Visualization Capabilities
Qlik offers rich and interactive data visualization tools. Various visualization options such as graphs, tables, maps, and dashboards facilitate understanding of complex data sets. Qlik’s drag-and-drop interface allows even non-technical users to create impressive visualizations.
Qlik’s Data Integration Solutions
Qlik offers powerful solutions for collecting and integrating data from different data sources. Tools such as Qlik Replicate and Qlik Compose automate data integration and transformation, providing clean and reliable data for descriptive analytics applications.
Qlik NPrinting
Qlik NPrinting is a reporting solution that transforms visualizations and analyses created on the Qlik platform into professional reports. This tool enables the sharing of insights across the organization by creating regularly updatable reports in PDF, Excel, and PowerPoint formats.
Challenges in Implementing Descriptive Analytics and Proposed Solutions
Implementation of descriptive analytics solutions may present various challenges for organizations. Understanding and proactively addressing these challenges is critical for a successful descriptive analytics strategy.
Data Quality Issues
The effectiveness of descriptive analytics largely depends on the quality of the data used. Missing, erroneous, or inconsistent data can lead to incorrect insights and decisions.
Proposed Solution: Creating a comprehensive data governance framework and implementing data quality control mechanisms can reduce data quality issues. Qlik’s data profiling and cleaning tools can help detect and address data quality problems.
Skills Gap
Expert personnel in data analysis, data visualization, and business intelligence are needed for effective descriptive analytics applications. The lack of professionals with these skills can limit the success of descriptive analytics initiatives.
Proposed Solution: Qlik’s intuitive and user-friendly interface enables even non-technical users to perform data analysis. Additionally, regular training programs and investments aimed at developing employees’ analytical skills can help close the skills gap.
Organizational Barriers
The success of descriptive analytics applications depends on organizational culture and structure. The absence of a data-driven culture and lack of interdepartmental collaboration can limit the effectiveness of descriptive analytics applications.
Proposed Solution: Qlik’s collaboration features facilitate the sharing of insights between different teams. Additionally, gaining the support of top management and encouraging a data-driven decision-making culture can help overcome organizational barriers.
The Future of Descriptive Analytics
Developments in the field of data analytics are shaping the future of descriptive analytics. Some important trends that will affect descriptive analytics in the coming years are:
AI-Powered Descriptive Analytics
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies will be increasingly used to enhance descriptive analytics processes. Tools like Qlik’s Insight Advisor automatically detect patterns and trends in data sets, providing users with valuable insights. These technologies will increase the effectiveness of descriptive analytics by enabling faster and deeper analyses.
Real-Time Analytics
The rapidly changing nature of the business world is increasing the demand for real-time descriptive analytics solutions. Qlik’s in-memory analytics engine enables real-time analysis of large data sets. In the future, real-time analyses of data from IoT devices and smart sensors will become an important part of descriptive analytics.
Self-Service Analytics
Self-service analytics solutions enable even non-technical users to perform their own data analyses. Qlik’s intuitive user interface and drag-and-drop features support self-service analytics applications. In the future, more advanced self-service analytics tools will further advance the democratization of analytics in organizations.
Conclusion
Descriptive Analytics is a powerful analytical approach that enables organizations to understand their past performance and evaluate their current situation. By answering the question “what happened?”, it forms the foundation of data-based decision-making processes. Modern business intelligence platforms like Qlik facilitate descriptive analytics applications, enabling organizations to derive maximum value from their data.
In today’s competitive business environment, descriptive analytics applications have become a necessity, not an option. With the right tools, technologies, and strategies, organizations can leverage the insights provided by descriptive analytics to make smarter decisions and gain competitive advantage. As the future of data analytics rapidly evolves, descriptive analytics will continue to be a fundamental component of data-driven decision-making processes.
References:
- Gartner, “Market Guide for Descriptive Analytics”, 2023
- McKinsey & Company, “The Age of Analytics: Competing in a Data-Driven World”, 2024
- IDC, “Worldwide Business Intelligence and Analytics Software Market Forecast”, 2023

