The systematic examination of financial data is critically important for making strategic decisions and assessing financial health in the business world. Financial Analysis is a methodological approach used to evaluate an organization’s financial condition, performance, and future expectations. Properly conducted financial analysis reveals a company’s strengths and weaknesses, identifies opportunities and threats, and establishes a solid foundation for long-term strategic decisions.
Core Components of Financial Analysis
Financial analysis is a comprehensive process consisting of various components. These components allow for the evaluation of a company’s financial situation from different perspectives.
Financial Statement Analysis
The financial analysis process essentially begins with examining financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. These statements provide a snapshot of the company’s financial position and provide basic data for evaluating its performance.
The balance sheet shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific date. The income statement summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and profit or loss during an accounting period. The cash flow statement tracks the company’s cash inflows and outflows.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting financial ratios obtained by comparing different items in financial statements. These ratios provide valuable information about the company’s liquidity position, profitability, debt repayment capacity, and operational efficiency.
According to Gartner’s 2023 report, 78% of companies that perform regular ratio analysis can take faster and more effective measures in financial crisis situations.
Cash Flow Analysis
Cash flow analysis involves evaluating a company’s cash inflows and outflows. Cash movements arising from the company’s operational activities, investment activities, and financing activities are examined separately. This analysis assesses the company’s capacity to generate cash and its ability to meet short-term financial obligations.
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis involves examining changes in financial data over time. By comparing financial data from multiple periods, trends in the company’s financial performance are identified. This analysis helps visualize the company’s growth rate, profitability trends, and changes in other important financial indicators.
Types of Financial Analysis
Financial analysis can be performed in various types, each allowing for the evaluation of financial data from different perspectives.
Horizontal Analysis
Horizontal analysis involves comparing financial statements from consecutive periods. This type of analysis evaluates changes in financial data as absolute values and percentages. For example, how a company’s sales revenues have changed over the last five years can be examined using the horizontal analysis method.
Vertical Analysis
Vertical analysis involves expressing each item in a financial statement as a percentage relative to a specific reference value. For example, in the balance sheet, each item can be compared to total assets, while in the income statement, each item can be compared to net sales. This analysis helps understand the structure of financial statements and facilitates comparing companies of different sizes.
Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis evaluates a company’s performance by establishing mathematical relationships between different financial items. Various financial ratios provide insights into the company’s liquidity position, profitability, efficiency, and debt repayment capacity.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis involves comparing a company’s financial data with its competitors’ data or industry averages. This analysis helps assess the company’s position and competitive strength in the industry.
Key Ratios Used in Financial Analysis
Various financial ratios used in the financial analysis process allow for the evaluation of the company from different perspectives. These ratios are generally divided into four main categories.
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios measure a company’s capacity to meet its short-term obligations. The most common liquidity ratios are:
- Current Ratio: Ratio of current assets to short-term liabilities
- Acid-Test Ratio (Quick Ratio): Ratio of current assets excluding inventory to short-term liabilities
- Cash Ratio: Ratio of cash and cash equivalents to short-term liabilities
According to McKinsey’s 2024 report, companies with strong liquidity ratios tend to be 45% more resilient against economic fluctuations.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios assess a company’s ability to generate profit. Common profitability ratios include:
- Gross Profit Margin: Ratio of gross profit to net sales
- Net Profit Margin: Ratio of net profit to net sales
- Return on Equity (ROE): Ratio of net profit to equity
- Return on Assets (ROA): Ratio of net profit to total assets
Activity Ratios
Activity ratios measure how efficiently a company uses its assets. These ratios include:
- Inventory Turnover Rate: Ratio of cost of goods sold to average inventory
- Accounts Receivable Turnover Rate: Ratio of net sales to average trade receivables
- Asset Turnover Rate: Ratio of net sales to total assets
Leverage Ratios
Leverage ratios assess a company’s debt repayment capacity and capital structure. Common leverage ratios include:
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Ratio of total debt to equity
- Financial Leverage Ratio: Ratio of total assets to equity
- Interest Coverage Ratio: Ratio of earnings before interest and taxes to interest expenses
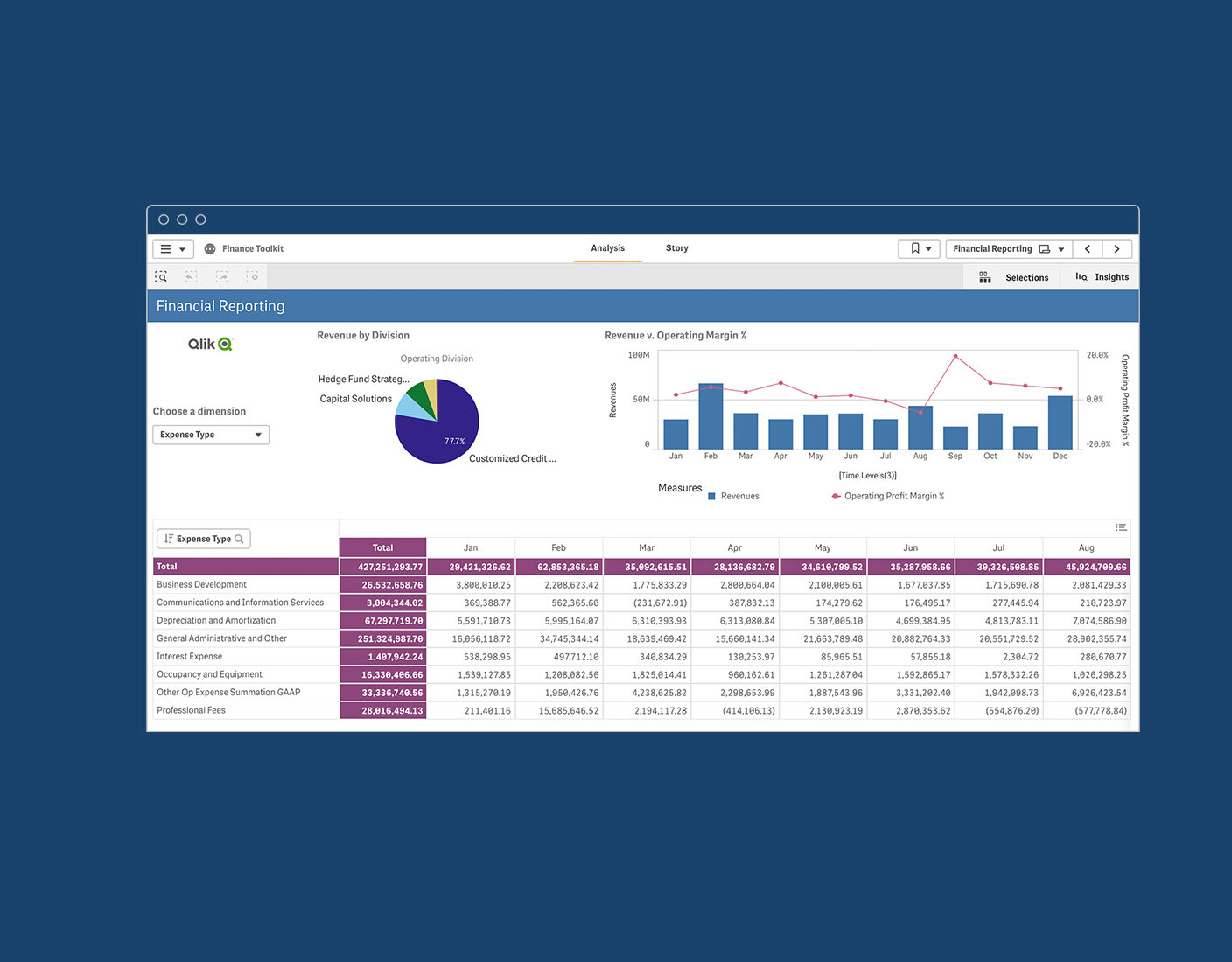
Financial Analysis Process
An effective financial analysis process requires a systematic approach and generally includes the following steps.
Data Collection
The financial analysis process begins with collecting relevant financial data. This data can be obtained from various sources such as the company’s financial statements, industry reports, macroeconomic data, and the company’s strategic plans.
Data Processing and Analysis
Collected data is processed using various analysis techniques. At this stage, financial ratios are calculated, trends are identified, and comparative analyses are performed. Modern analysis tools and software can significantly facilitate the data processing process at this stage.
Interpretation of Results
Analysis results are interpreted to provide insights into the company’s financial condition, performance, and future expectations. These interpretations help identify the company’s strengths and weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Reporting
Finally, analysis findings and interpretations are reported for presentation to decision-makers. These reports may include graphics, tables, and explanatory texts and are generally supported by action recommendations.
Financial Analysis Solutions with Qlik
Qlik offers advanced data analytics solutions to optimize and deepen financial analysis processes. These solutions allow for more effective analysis of financial data and improvement of decision-making processes.
Financial Data Visualization
Qlik’s advanced visualization capabilities enable complex financial data to be transformed into understandable and actionable insights. Interactive graphs, heat maps, and dashboards help quickly detect financial trends and anomalies.
Interactive Reporting
Qlik’s interactive reporting features allow users to explore financial data dynamically. Users can perform drill-down analyses, compare different time periods, and create their own custom queries.
Real-Time Financial Analysis
Qlik enables the real-time integration and analysis of financial data from different sources. This allows for real-time monitoring of the financial situation and proactive response to rapidly changing market conditions.
Financial Planning and Forecasting
Qlik’s advanced analytical capabilities facilitate creating future financial performance forecasts based on historical financial data. What-if analyses and scenario modeling help evaluate the potential financial impacts of different strategic options.
Challenges in Financial Analysis Applications and Solution Proposals
Various challenges may be encountered in financial analysis processes. Understanding and proactively addressing these challenges is critical for more effective financial analysis.
Data Quality Issues
The accuracy and reliability of financial analysis depend on the quality of the data used. Missing, erroneous, or inconsistent data can lead to misleading results.
Solution Proposal: Qlik’s data management features can help detect and correct data quality issues. Data quality can be improved by implementing automatic data validation checks and data cleaning processes.
Data Integration Challenges
Financial data often comes from ERP systems, accounting software, budget applications, and other sources. Integrating these different sources can create technical challenges.
Solution Proposal: Qlik’s data integration capabilities enable seamless combination of data from different sources. Tools such as Qlik Sense and Qlik Data Integration can connect to various data sources and transform data into a single consistent view.
Developing Analytical Capabilities
Financial analysis requires both technical skills and financial knowledge. Lack of these skills can limit the effectiveness of analysis processes.
Solution Proposal: Qlik’s user-friendly interface and self-service analytics capabilities allow even non-technical users to perform financial analyses. Additionally, Qlik training programs and community resources can help develop analytical skills.
The Future of Financial Analysis
The field of financial analysis is rapidly evolving with technological developments. Some important trends that will shape this field in the coming years include:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies will be increasingly used to automate and deepen financial analysis processes. These technologies can provide significant advantages in areas such as anomaly detection, trend prediction, and risk assessment.
Automated Financial Insights
Advanced analytical tools will be able to automatically detect patterns in financial data and provide important insights to decision-makers. This will enable the automation of routine financial analyses and allow financial analysts to focus on more strategic tasks.
Predictive Financial Analytics
Predictive analytics technologies will be more widely used to forecast future financial performance based on historical financial data. This will enable companies to take proactive measures and make more informed strategic decisions.
Conclusion
Financial Analysis is a process of critical importance for evaluating companies’ financial health, measuring performance, and developing strategies for the future. Core components such as financial statement analysis, ratio analysis, cash flow analysis, and trend analysis allow for the evaluation of the company from different perspectives.
Modern data analytics platforms like Qlik can provide more accurate and actionable insights by optimizing, deepening, and automating financial analysis processes. These tools enhance the effectiveness and value of financial analysis with capabilities such as data integration, visualization, interactive reporting, and forecasting.
With technological developments and changing business requirements, the field of financial analysis will continue to evolve. The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics into financial analysis processes is among the important trends that will shape the future of this field.
References:
- Gartner, “Market Guide for Financial Analytics”, 2023
- McKinsey & Company, “The Future of Financial Analysis”, 2024
- Qlik, “Financial Analysis Solutions”, 2023

